Python Lambda Functions
Page Info
Content
Python Lambda Functions
In Python, lambda functions are anonymous, one-line functions defined using the syntax lambda parameters: expression. They are useful for short operations, passing functions as arguments, or when you want a concise function without using def.
Basic Syntax
lambda arguments: expressionExplanation:
- lambda: Keyword to define an anonymous function.
- arguments: One or more parameters passed to the function.
- expression: The operation performed using the arguments, whose result is returned.
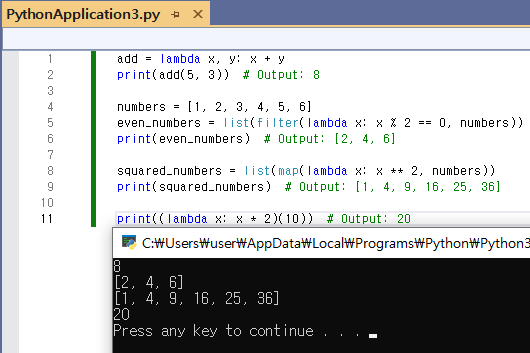
Example 1: Sum of Two Numbers
add = lambda x, y: x + y
print(add(5, 3)) # Output: 8
Example 2: Filtering Even Numbers from a List
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
even_numbers = list(filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
print(even_numbers) # Output: [2, 4, 6]
Example 3: Squaring Elements of a List
squared_numbers = list(map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers))
print(squared_numbers) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
Example 4: Immediate Execution of Lambda
print((lambda x: x * 2)(10)) # Output: 20
Why Use Lambda Functions
- Conciseness: Define small functions in a single line.
- Anonymous: Functions without a name for clean code, especially as arguments to other functions.
- Convenience: Works seamlessly with
map(),filter(),sorted(), and other higher-order functions.
SEO Keywords
Python lambda, anonymous function Python, lambda example Python, Python one-line function, Python map filter lambda, Python functional programming
Use lambda functions in Python for concise, readable, and efficient code when you need small, single-expression functions.
Good0 Bad0
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.
